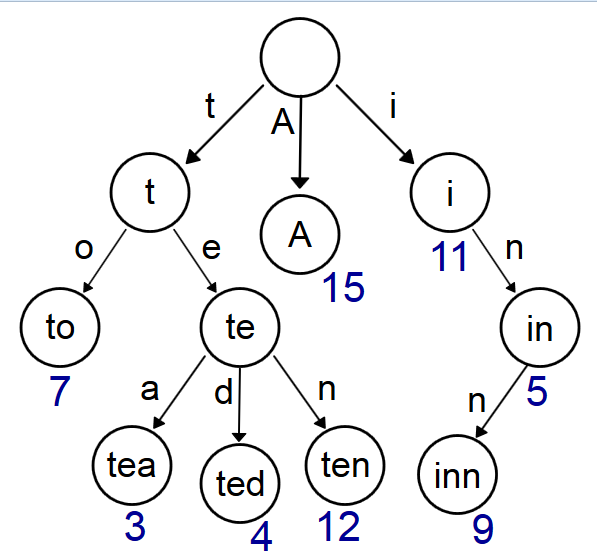
A Merkle Patricia Trie (just called trie from now on) is a data strcture that functions as a key value store, but has two important properties:
- simple and efficient verification of data integrity
- proof that the trie contains a key/value pair
The trie structure accomplishes this by creating a branching data structure. By starting at the root, then following the branches while using the key to select which branches to take, you will end up at the value. To create this structure in an efficient way, the trie uses 4 different kind of nodes:
- empty
- branch
- extension
- leaf
https://eth.wiki/fundamentals/patricia-tree https://medium.com/@chiqing/merkle-patricia-trie-explained-ae3ac6a7e123
Branch node
A branch node splits into 16 different directions.
Extension node
An extension node is a kind of portal, it skips a part of the path that doesn’t contain any branches or leafs.
Leaf node
The leaf node is a terminating node. This only contains the remaining path and the value.
Getting a value
To get a value, we need to recursively navigate the trie nodes:
- start at the root
- if we reach a branch, choose the correct path or return the value if it’s a match
- if we reach an extension, skip forward to the next node
- if we reach a leaf, return the value
- if we reach an empty node, return null
Putting a value
To put a new value value into the trie, we need to follow the following steps to create and update the nodes in the trie:
- start at the root
- if we reach an empty node, create a new leaf node with the value
- if we reach a branch, choose and set the correct path or set the value if it’s a match
- if we reach an extension, shorten it and add a branch or skip forward if it’s a match
- if we reach a leaf, create a branch or set the value if it’s a match
This process is done recursively, and each visited node is updated on the way up. This means that each put operation updates and entire branch, including the root node.
Deleting a value
To delete a value, we recursively go down a branch until we reach it, then we remove it and update all nodes above. If nodes are made empty because of the deleting, those nodes are also removed or simplified. For example, when a branch only has one value left, it is turned into a leaf node.